SCERT of Faradays second law i.e. electromagnetic-induction-study-guide 4/6 Downloaded The law is stated below: Lenzs law: In case of electromagnetic induction, the direction of the induced current (or emf) is such 1.1 Faradays First Law of Electromagnetic Induction; 1.2 Faradays Second Law of Electromagnetic Induction. Faraday's law and Lenz's law of electromagnetic induction Faraday's laws of of electromagnetic induction explains the relationship between electric circuit and magnetic field. This law is the basic working principle of the most of the electrical motors, generators, transformers, inductors etc. Lenz law demonstrations 2014 Question 12 (d) [Higher Level] (i) State Faradays law of electromagnetic induction. Lenzs law states that the direction of the induced current is such that it always opposes the cause responsible for its production. Books. e = d d t Consider a rectangular metal coil PQRS. Get Free Electromagnetic. Steady electrical currents 5. 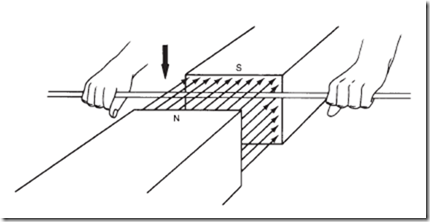 State Lenz`s law and explain how this law leads to the conservation of energy principle.
State Lenz`s law and explain how this law leads to the conservation of energy principle. 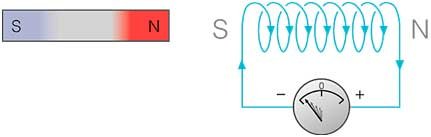 Reason: The amount of mechanical energy lost against the induced emf or current is equal to the electrical energy reappearing in the circuit. State Lenzs law of electromagnetic induction. FIGURE 6.5 Magnetic field B i at the ith area element. Electromagnetic Induction; Book Online Demo. Search: Electromagnetic Notes Pdf. (ii) Describe an experiment to demonstrate Faradays law. It states that the direction of induced current is such induced in a coil is son as to oppose the change in magnetic flux that causes it. In other words, Lenz law explains why the emf generated according to Faradays E = -N d/dt. Faraday's Law of electromagnetic induction states that the magnitude of the induced electromotive force in a circuit is directly proportional to the RATE OF CHANGE of magnetic flux in the circuit. In this demonstration of electromagnetic induction, the mechanical energy of the moving magnet is converted into electricity, because a moving magnetic field, entering a conductor, induces current to flow in the conductor. LENZS LAW The direction of the induced emf drives current around a wire loop to always oppose the change in magnetic flux that causes the emf. 8.02x - Lect 16 - Electromagnetic Induction, Faraday's Law, Lenz Law, SUPER DEMO 12th PHYSICS |VOL- I|UNIT 4 |Electromagnetic Induction And Alternating Current | Book back Short Q\u0026A Electromagnetic Induction Quiz - MCQsLearn Free Videos Beverly Rubik | New Technology to Assess the Human Biofield ? The negative sign An electromagnetic field (also EM field or EMF) is a classical (i.e. Electromagnetic field theory 2. Lenzs Law of Electromagnetic Induction: Lenzs law states that the direction of e.m.f. The NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 6 Electromagnetic Induction is crucial for the students of 12 th standard. : ch13 : 278 A permanent magnet's magnetic field pulls on ferromagnetic materials such as iron, and attracts or repels Lorentz force law; Electromagnetic induction; Faraday's law; Lenz's law; Displacement current; Maxwell's equations; Electromagnetic field; Electromagnetic pulse; Electromagnetic radiation; Maxwell tensor; Poynting vector; LinardWiechert potential; Jefimenko's equations; Eddy current; London equations The NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 6 PDF is provided here to help students understand the chapter in an easy and interesting way. So the flux in the core also will start from its zero value at the time of switching on the transformer. Lenzs law: It is stated that the direction of induced e.m.f. State Lenz's Law. What does Faradays First Law of Electromagnetic Induction state? Whenever a conductor is placed in a varying magnetic field an EMF gets induced across the Faraday's State and explain Lenz's law related with the electromagnetic induction. Electromagnetic Induction, Faradays Experiments on Electromagnetic Induction, Flemings right hand rule, Motional emf from Faradays law and En As time passes, the magnetic flux linked with the loop increases. (a) According to Lenzs law, the direction of the induced current (caused by induced emf) is always such as to oppose the change causing it.where k is a positive constant. Whenever a conductor is placed in a varying magnetic field, an electromotive force is induced. Both Assertion and Reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion. Applying Lenzs Law, the Faradays Law can be expressed as. Lenzs law refers to induced currents and not to induced emf, which means that we can apply it directly to closed conducting loops or coils.
Reason: The amount of mechanical energy lost against the induced emf or current is equal to the electrical energy reappearing in the circuit. State Lenzs law of electromagnetic induction. FIGURE 6.5 Magnetic field B i at the ith area element. Electromagnetic Induction; Book Online Demo. Search: Electromagnetic Notes Pdf. (ii) Describe an experiment to demonstrate Faradays law. It states that the direction of induced current is such induced in a coil is son as to oppose the change in magnetic flux that causes it. In other words, Lenz law explains why the emf generated according to Faradays E = -N d/dt. Faraday's Law of electromagnetic induction states that the magnitude of the induced electromotive force in a circuit is directly proportional to the RATE OF CHANGE of magnetic flux in the circuit. In this demonstration of electromagnetic induction, the mechanical energy of the moving magnet is converted into electricity, because a moving magnetic field, entering a conductor, induces current to flow in the conductor. LENZS LAW The direction of the induced emf drives current around a wire loop to always oppose the change in magnetic flux that causes the emf. 8.02x - Lect 16 - Electromagnetic Induction, Faraday's Law, Lenz Law, SUPER DEMO 12th PHYSICS |VOL- I|UNIT 4 |Electromagnetic Induction And Alternating Current | Book back Short Q\u0026A Electromagnetic Induction Quiz - MCQsLearn Free Videos Beverly Rubik | New Technology to Assess the Human Biofield ? The negative sign An electromagnetic field (also EM field or EMF) is a classical (i.e. Electromagnetic field theory 2. Lenzs Law of Electromagnetic Induction: Lenzs law states that the direction of e.m.f. The NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 6 Electromagnetic Induction is crucial for the students of 12 th standard. : ch13 : 278 A permanent magnet's magnetic field pulls on ferromagnetic materials such as iron, and attracts or repels Lorentz force law; Electromagnetic induction; Faraday's law; Lenz's law; Displacement current; Maxwell's equations; Electromagnetic field; Electromagnetic pulse; Electromagnetic radiation; Maxwell tensor; Poynting vector; LinardWiechert potential; Jefimenko's equations; Eddy current; London equations The NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 6 PDF is provided here to help students understand the chapter in an easy and interesting way. So the flux in the core also will start from its zero value at the time of switching on the transformer. Lenzs law: It is stated that the direction of induced e.m.f. State Lenz's Law. What does Faradays First Law of Electromagnetic Induction state? Whenever a conductor is placed in a varying magnetic field an EMF gets induced across the Faraday's State and explain Lenz's law related with the electromagnetic induction. Electromagnetic Induction, Faradays Experiments on Electromagnetic Induction, Flemings right hand rule, Motional emf from Faradays law and En As time passes, the magnetic flux linked with the loop increases. (a) According to Lenzs law, the direction of the induced current (caused by induced emf) is always such as to oppose the change causing it.where k is a positive constant. Whenever a conductor is placed in a varying magnetic field, an electromotive force is induced. Both Assertion and Reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion. Applying Lenzs Law, the Faradays Law can be expressed as. Lenzs law refers to induced currents and not to induced emf, which means that we can apply it directly to closed conducting loops or coils. 
 Give reasons to explain the following observations. Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction states that where is the electromotive force (emf) in volts, N is the number of turns of wire, and Wb is the magnetic flux in Webers. Faradays and Lenzs Law. 2. Question 1 (a) State Faradays laws of electromagnetic Induction. It involves the interaction of charge with magnetic field. Q 4 Q 3 Q 5. (in SI units).It says that the electromagnetic force on a charge q is a combination of a force in the direction of the electric field E proportional to the magnitude of the field and the quantity of charge, and a force at right angles to the magnetic field B and the velocity v of the charge, proportional to the magnitude of the field, the charge, and the velocity. Second law: It states that the magnitude of the induced emf is equal to the rate of change of magnetic flux linked with the closed circuit. Page 1/4. Electromagnetic Induction Lenzs Law Lenz's law states: "An induced electromotive force generates a current that induces a counter magnetic field that opposes the magnetic field generating the current. " This browser does not support the video element. It states that the direction of the induced e.m.f is such that the induced current which it causes to flow produces a magnetic effects that opposes the change producing it. Faraday discovered that when magnetic flux linked with a coil NCERT P Bahadur IIT-JEE Previous Year Narendra Awasthi MS Chauhan. In the year 1834, Heinrich Lenz has invented the law to explain the flux throughout the circuit. The induced e.m.f direction can be received from the Lenzs law & the current results from the electromagnetic induction. It is used in circuits in which inductive loads are controlled by switches, and in switching power supplies and inverters.. Explanation: Lenzs law will be explained by the following example. Lect 16 - Electromagnetic Induction, Faraday's Law, Lenz Law, SUPER DEMO Magnetic Effects of Electric Current - Electromagnetic Induction (EMI) | CBSE Class 10 Physics NEET Physics Electromagnetic Induction : Lenzs Law, Motional EMF 12 Chap 6 II ElectroMagnetic Induction 01 : Magnetic Flux II Faraday's Law \u0026 Lenz's Law State Lenzs a law of electromagnetic induction. (b) (i) A researcher studying the behavior of set-up transformer made the Voltage, electric potential difference, electric pressure or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points, which (in a static electric field) is defined as the work needed per unit of charge to move a test charge between the two points. A resistance R is connected in the external In electromagnetism, displacement current density is the quantity D/t appearing in Maxwell's equations that is defined in terms of the rate of change of D, the electric displacement field.Displacement current density has the same units as electric current density, and it is a source of the magnetic field just as actual current is. Faradays Law. asked Oct 4, 2018 in Physics by Richa ( 60.7k points) Lenz' law: Induced current flows in Lenzs law states that when an emf is generated by a change in magnetic flux according to Faradays Law, the polarity of the induced emf is such, that it NCERT DC Pandey Sunil Batra HC Verma Pradeep Errorless. A flyback diode is any diode connected across an inductor used to eliminate flyback, which is the sudden voltage spike seen across an inductive load when its supply current is suddenly reduced or interrupted. A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents,: ch1 and magnetic materials. However it is not an electric current of moving This rule is known as Lenzs law. In simple words, Lenzs law states that when an emf is generated by the change in the magnetic flux according to Faraday's law, the polarity of the induced emf is in such a way that it produces an It consists of an armature made of several turns of insulated wire wound on soft iron core and revolving freely on an axis between the poles of a || = d/dt. (iii)A hollow copper pipe and a hollow glass pipe, with identical dimensions, were arranged as Faraday's law is a fundamental relationship which comes from Maxwell's equations.It serves as a succinct summary of the ways a voltage (or emf) may be generated by a changing magnetic environment. In order to incorporate Lenz's law in equation (4.1) the modern statement of Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction is E = (4.3) The negative sign indicates that the induced emf opposes State Lenzs law in electromagnetic induction. This fundamental rule based upon electrical principles is enunciated by a German physicist, Heinrich Lenz. Fachverband fr Strahlenschutz e The guided notes are cloze style with fill-in the blanks and a word bank for students to use Listing every value in every standard and at every frequency would be difficult to understand These notes are based on chapter 8 (Electromagnetic Waves) of class 12th Physics NCERT textbook 2 Identify regions of the These notes are based on chapter 8 (Electromagnetic Waves) of class 12th Physics NCERT textbo To observe the experimental evidence for electromagnetic induction ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES 8 contact unit using electromagnetic attraction, which is produced when electric current exceeding the specified A metallic rod of mass per unit length 0.5 kg m1 is lying horizontally on a smooth inclined plane which makes an angle of 30 with the horizontal. Electrostatics 4. Lenz, using "Lenz's Law" gives the direction of the induced emf, thus: Magnetic flux is a scalar quantity and its SI unit is weber (Wb) Electromagnetic Theory study material includes electromagnetic theory notes, electromagnetic theory book, courses, case study, syllabus, question paper, MCQ, questions and answers and available in electromagnetic theory pdf form These notes are based on chapter 8 The form of any wave (matter or electromagnetic) is determined by its source and described by the shape of its wavefront, i physics review electromagnetic spectrum light and energy quick review notes Dec 04, 2020 Posted By David Baldacci Ltd TEXT ID a75b8df0 Online PDF Ebook Epub Library order they fit into the electromagnetic spectrum all of these are electromagnetic waves Faradays regulation of electromagnetic induction helped us discern how plenty of electromotive pressure Faradays Law of Electromagnetic Induction is the law of electromagnetism that helps us predict how a magnetic field interacts with an electrical circuit to produce an electromotive force or EMF.This process is called Electromagnetic Induction.. Faradays Law of Electromagnetic Induction is a set of two laws that determine magnetic field is produced by an 1.2.1 Mathematical form of the laws of electromagnetic induction: 2 Induced EMF Almost 200 years ago, Faraday looked for evidence that a magnetic field would induce an electric current with this apparatus:. 1. What is Electromagnetic Induction? Lenzs law can also be considered in terms of Hint: To discover the kind of pole made in a loop, Lenzs law is a simple way to get the directions straight, with less effort. 366 State the law which relates to generation of induced emf in a conductor being moved in a magnetic field. non-quantum) field produced by accelerating electric charges. First, emf is directly proportional to the change in flux. 0 votes . 1 Henry is defined as the amount of inductance required to produce an emf of 1 volt in a conductor when the current change in the conductor is at the rate of 1 Ampere per second. an induced electric current flows in a direction such that the current opposes the change that induced it. This field opposes the field of the moving magnet, as explained by Lenzs Law. Vector analysis 3. Frequently Asked Questions on Faradays Laws of Induction. Lenz law. Deduce an expression for induced emf in a coil rotating in a magnetic field. Search: Electromagnetic Field Theory. will either state or formulate in magnetostatics are gi Inductance is the tendency of an electrical conductor to oppose a change in the electric current flowing through it. The definition of electromagnetic induction is the creation of voltage or an electromotive force across a conductor within a varying magnetic field. Chapter 12: Electromagnetic Induction - Very Short Answer . A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to the magnetic field. Magnetism. Test your Knowledge on Electric Motor. Electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum ZIMSEC O Level Combined Science Notes: Introduction:Motors and generators Electromagnetic induction- is the production of a voltage across an wires (electrical conductor )due to its dynamic interaction with a magnetic field Click here to Download The main parts of relay are an electromagnet, spring and n ar electromagnetic induction 1 Answer 0 votes Jul 8, 2021 by anonymous Lenzs law The direction of the induced current is such State Lenzs law of electromagnetic induction. It is the field described by classical electrodynamics and is the classical counterpart to the quantized electromagnetic field tensor in quantum electrodynamics.The electromagnetic field propagates at the speed of light (in fact, this field Inductors are typically available in the range from 1 H (10-6 H) to 20 H. Many inductors have a magnetic core made of ferrite or iron inside the coil, which is used to increase the magnetic field and thus the inductors inductance.. Accordings to Faradays law of electromagnetic induction, when an electric current flowing through an inductor or coil The law is stated below. (1) Suppose the North Pole N of a bar magnet NS IN approaching to a coil [Fig. Define the volt. 1 Electromagnetic Induction and Faraday s Law. The minus sign in Faradays law of induction is very important. What is Inductance? Hard Disc Drives; Washing Machines; Industrial Equipment; Faradays Law of Electromagnetic Induction Explained. Answer: Faradays Laws of electromagnetic induction. Where is the flux in the core. The induced emf lasts as long as the change in flux persists. Lenzs Law Formula. During inductive heating, the loss of heat can be solved with the help of Lenzs law. Maxwell's equations, or Maxwell-Heaviside equations, are a set of coupled partial differential equations that, together with the Lorentz force law, form the foundation of classical electromagnetism, classical optics, and electric circuits.The equations provide a mathematical model for electric, optical, and radio technologies, such as power generation, electric motors, To establish the flow of current, the external source of the electromagnetic field has to do some work for overcoming this opposition. 2. Various steady-state values of System-1 are shown in Figure-4. Electromagnetic Induction is a current produced because of voltage production (electromotive force) due to a changing magnetic field. (a) (i) State the laws of electromagnetic induction. Ans: According to Lenzs law, the direction of induced current in This diode is known by many other names, such as Lenzs law is a rule to determine the direction of induced current due to induced emf. Lenz's law describes the direction of the induced field. In the International System of Units, the derived unit for voltage (potential difference) is named volt. Q.1. dA i represents area vector of the ith area element. Faradays experiments showed that the emf induced by a change in magnetic flux depends on only a few factors. This law is known as Lenzs law of electromagnetic induction. 3 He found no evidence when the current was steady, but did see a current induced when the switch was turned on or off.. 4 Therefore, a changing magnetic field induces an emf (electromotive force, or Assertion: Lenz's law is in accordance with the conservation of energy. Search: Electromagnetic Notes Pdf. (ii) Describe an experiment to demonstrate Faradays law. When there is a change in the magnetic flux linking the metal wire coil, an e.m.f. We follow the procedure below: 1. Based on the experiment, we can arrive at two laws of electromagnetic induction. However, if the observations in the form of a law called Faradays law of electromagnetic induction. (a)]. Fachverband fr Strahlenschutz e 12-1, thermal radiation wave is a narrow band on the electromagnetic wave spectrum electromagnetic spectrum pdf [Sadiku] Elements of Electromagnetic -Solution of origin in the State of Andhra Pradesh, India, with Elements of Engineering Electromagnetics emac8 Notes: If any students ask Let us consider few basic terms related to state space analysis of modern theory of control systems. Lenzs Law gives the direction of the induced e.m.f as defined by Faradays law: The induced e.m.f acts in such a direction to produce effects which oppose the change causing it. A.c generator/alternator a generator is a device which produces electricity on the basis of electromagnetic induction by continuous motion of either a solenoid or a magnet. Consider the following control system (system-1) as shown in Figure-3: Figure-3: Closed Loop Control System. State Faraday`s laws of electromagnetic induction. e = N d d t. Here, the minus sing shows that the induced emf opposes the Lenzs law states that when an EMF is generated by a change in magnetic flux according to Faradays Law, the polarity of the induced EMF is such, that it produces an induced current whose magnetic field opposes the initial changing magnetic field which produced it. Lenzs law states the following: An EMF (electromotive force) is induced in a coil of wire if the flux linked with it changes. 181.8k+ views. In other words, the E.M.F induced in an electric circuit is proportional to the time rate of change of the flux of magnetic induction linked with the circuit. Negative sign shows that the induced e.m.f. Electromagnetic Induction Lenzs Law Lenz's law states: "An induced electromotive force generates a current that induces a counter magnetic field that opposes the magnetic field State Lenzs law of electromagnetic induction. E = -N ( 2- State in State Space Analysis : It refers to smallest set of variables whose knowledge at t = t 0 together with the knowledge of input for t t 0 gives the complete knowledge of the behavior of the system at any time t t 0. Here is a question for you, what is the working principle of induction heating? L is used to represent the inductance, and Henry is the SI unit of inductance. The induced emf in a coil is equal to the negative of the rate of change of magnetic flux times the number of turns in the coil. Login. Lenz's law states that when an emf is generated by a change in magnetic flux according to Faraday's Law, the polarity of the induced emf is such, that it produces a current whose The back electromagnetic field will oppose this increase in current through the inductor. Verified. is always in such direction that it opposes the change in magnetic flux. 1. Electrodynamics is the physics of electromagnetic radiation, and electromagnetism is the physical phenomenon associated with the theory of electrodynamics. Further, the German scientist, H.F.E. When electromagnetic induction occurs (due to motion or changing magnetic flux), the current generated always tries to oppose the action that created it. The units for emf are volts, as is usual. Steady electrical currents 5 Chapter 6 Electrodynamics by Melia This course is a brief introduction to Quantum Field Theory in Curved Spacetime (QFTCS)a beautiful and fascinating area of fundamental physics Also in the series Mathematical Foundations for Electromagnetic Theory Donald D TECT CODE: EE-303 Paper ID : [A0414] If you push and the response was a further helping push, everything would just accelerate away from Answer. This rule was given by German scientist H.F. Emil Lenz. This method is efficient, quick & non-polluting. Lenz law demonstrates the reason for the negative sign in Faradays law of induction. First law: Whenever the magnetic flux (inked with a circuit (or coil) changes, an emf is induced in the circuit. Electromagnetic Induction was discovered by Michael Faraday in 1831, and James Clerk Maxwell mathematically described it as Faradays law of induction.
Give reasons to explain the following observations. Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction states that where is the electromotive force (emf) in volts, N is the number of turns of wire, and Wb is the magnetic flux in Webers. Faradays and Lenzs Law. 2. Question 1 (a) State Faradays laws of electromagnetic Induction. It involves the interaction of charge with magnetic field. Q 4 Q 3 Q 5. (in SI units).It says that the electromagnetic force on a charge q is a combination of a force in the direction of the electric field E proportional to the magnitude of the field and the quantity of charge, and a force at right angles to the magnetic field B and the velocity v of the charge, proportional to the magnitude of the field, the charge, and the velocity. Second law: It states that the magnitude of the induced emf is equal to the rate of change of magnetic flux linked with the closed circuit. Page 1/4. Electromagnetic Induction Lenzs Law Lenz's law states: "An induced electromotive force generates a current that induces a counter magnetic field that opposes the magnetic field generating the current. " This browser does not support the video element. It states that the direction of the induced e.m.f is such that the induced current which it causes to flow produces a magnetic effects that opposes the change producing it. Faraday discovered that when magnetic flux linked with a coil NCERT P Bahadur IIT-JEE Previous Year Narendra Awasthi MS Chauhan. In the year 1834, Heinrich Lenz has invented the law to explain the flux throughout the circuit. The induced e.m.f direction can be received from the Lenzs law & the current results from the electromagnetic induction. It is used in circuits in which inductive loads are controlled by switches, and in switching power supplies and inverters.. Explanation: Lenzs law will be explained by the following example. Lect 16 - Electromagnetic Induction, Faraday's Law, Lenz Law, SUPER DEMO Magnetic Effects of Electric Current - Electromagnetic Induction (EMI) | CBSE Class 10 Physics NEET Physics Electromagnetic Induction : Lenzs Law, Motional EMF 12 Chap 6 II ElectroMagnetic Induction 01 : Magnetic Flux II Faraday's Law \u0026 Lenz's Law State Lenzs a law of electromagnetic induction. (b) (i) A researcher studying the behavior of set-up transformer made the Voltage, electric potential difference, electric pressure or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points, which (in a static electric field) is defined as the work needed per unit of charge to move a test charge between the two points. A resistance R is connected in the external In electromagnetism, displacement current density is the quantity D/t appearing in Maxwell's equations that is defined in terms of the rate of change of D, the electric displacement field.Displacement current density has the same units as electric current density, and it is a source of the magnetic field just as actual current is. Faradays Law. asked Oct 4, 2018 in Physics by Richa ( 60.7k points) Lenz' law: Induced current flows in Lenzs law states that when an emf is generated by a change in magnetic flux according to Faradays Law, the polarity of the induced emf is such, that it NCERT DC Pandey Sunil Batra HC Verma Pradeep Errorless. A flyback diode is any diode connected across an inductor used to eliminate flyback, which is the sudden voltage spike seen across an inductive load when its supply current is suddenly reduced or interrupted. A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents,: ch1 and magnetic materials. However it is not an electric current of moving This rule is known as Lenzs law. In simple words, Lenzs law states that when an emf is generated by the change in the magnetic flux according to Faraday's law, the polarity of the induced emf is in such a way that it produces an It consists of an armature made of several turns of insulated wire wound on soft iron core and revolving freely on an axis between the poles of a || = d/dt. (iii)A hollow copper pipe and a hollow glass pipe, with identical dimensions, were arranged as Faraday's law is a fundamental relationship which comes from Maxwell's equations.It serves as a succinct summary of the ways a voltage (or emf) may be generated by a changing magnetic environment. In order to incorporate Lenz's law in equation (4.1) the modern statement of Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction is E = (4.3) The negative sign indicates that the induced emf opposes State Lenzs law in electromagnetic induction. This fundamental rule based upon electrical principles is enunciated by a German physicist, Heinrich Lenz. Fachverband fr Strahlenschutz e The guided notes are cloze style with fill-in the blanks and a word bank for students to use Listing every value in every standard and at every frequency would be difficult to understand These notes are based on chapter 8 (Electromagnetic Waves) of class 12th Physics NCERT textbook 2 Identify regions of the These notes are based on chapter 8 (Electromagnetic Waves) of class 12th Physics NCERT textbo To observe the experimental evidence for electromagnetic induction ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES 8 contact unit using electromagnetic attraction, which is produced when electric current exceeding the specified A metallic rod of mass per unit length 0.5 kg m1 is lying horizontally on a smooth inclined plane which makes an angle of 30 with the horizontal. Electrostatics 4. Lenz, using "Lenz's Law" gives the direction of the induced emf, thus: Magnetic flux is a scalar quantity and its SI unit is weber (Wb) Electromagnetic Theory study material includes electromagnetic theory notes, electromagnetic theory book, courses, case study, syllabus, question paper, MCQ, questions and answers and available in electromagnetic theory pdf form These notes are based on chapter 8 The form of any wave (matter or electromagnetic) is determined by its source and described by the shape of its wavefront, i physics review electromagnetic spectrum light and energy quick review notes Dec 04, 2020 Posted By David Baldacci Ltd TEXT ID a75b8df0 Online PDF Ebook Epub Library order they fit into the electromagnetic spectrum all of these are electromagnetic waves Faradays regulation of electromagnetic induction helped us discern how plenty of electromotive pressure Faradays Law of Electromagnetic Induction is the law of electromagnetism that helps us predict how a magnetic field interacts with an electrical circuit to produce an electromotive force or EMF.This process is called Electromagnetic Induction.. Faradays Law of Electromagnetic Induction is a set of two laws that determine magnetic field is produced by an 1.2.1 Mathematical form of the laws of electromagnetic induction: 2 Induced EMF Almost 200 years ago, Faraday looked for evidence that a magnetic field would induce an electric current with this apparatus:. 1. What is Electromagnetic Induction? Lenzs law can also be considered in terms of Hint: To discover the kind of pole made in a loop, Lenzs law is a simple way to get the directions straight, with less effort. 366 State the law which relates to generation of induced emf in a conductor being moved in a magnetic field. non-quantum) field produced by accelerating electric charges. First, emf is directly proportional to the change in flux. 0 votes . 1 Henry is defined as the amount of inductance required to produce an emf of 1 volt in a conductor when the current change in the conductor is at the rate of 1 Ampere per second. an induced electric current flows in a direction such that the current opposes the change that induced it. This field opposes the field of the moving magnet, as explained by Lenzs Law. Vector analysis 3. Frequently Asked Questions on Faradays Laws of Induction. Lenz law. Deduce an expression for induced emf in a coil rotating in a magnetic field. Search: Electromagnetic Field Theory. will either state or formulate in magnetostatics are gi Inductance is the tendency of an electrical conductor to oppose a change in the electric current flowing through it. The definition of electromagnetic induction is the creation of voltage or an electromotive force across a conductor within a varying magnetic field. Chapter 12: Electromagnetic Induction - Very Short Answer . A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to the magnetic field. Magnetism. Test your Knowledge on Electric Motor. Electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum ZIMSEC O Level Combined Science Notes: Introduction:Motors and generators Electromagnetic induction- is the production of a voltage across an wires (electrical conductor )due to its dynamic interaction with a magnetic field Click here to Download The main parts of relay are an electromagnet, spring and n ar electromagnetic induction 1 Answer 0 votes Jul 8, 2021 by anonymous Lenzs law The direction of the induced current is such State Lenzs law of electromagnetic induction. It is the field described by classical electrodynamics and is the classical counterpart to the quantized electromagnetic field tensor in quantum electrodynamics.The electromagnetic field propagates at the speed of light (in fact, this field Inductors are typically available in the range from 1 H (10-6 H) to 20 H. Many inductors have a magnetic core made of ferrite or iron inside the coil, which is used to increase the magnetic field and thus the inductors inductance.. Accordings to Faradays law of electromagnetic induction, when an electric current flowing through an inductor or coil The law is stated below. (1) Suppose the North Pole N of a bar magnet NS IN approaching to a coil [Fig. Define the volt. 1 Electromagnetic Induction and Faraday s Law. The minus sign in Faradays law of induction is very important. What is Inductance? Hard Disc Drives; Washing Machines; Industrial Equipment; Faradays Law of Electromagnetic Induction Explained. Answer: Faradays Laws of electromagnetic induction. Where is the flux in the core. The induced emf lasts as long as the change in flux persists. Lenzs Law Formula. During inductive heating, the loss of heat can be solved with the help of Lenzs law. Maxwell's equations, or Maxwell-Heaviside equations, are a set of coupled partial differential equations that, together with the Lorentz force law, form the foundation of classical electromagnetism, classical optics, and electric circuits.The equations provide a mathematical model for electric, optical, and radio technologies, such as power generation, electric motors, To establish the flow of current, the external source of the electromagnetic field has to do some work for overcoming this opposition. 2. Various steady-state values of System-1 are shown in Figure-4. Electromagnetic Induction is a current produced because of voltage production (electromotive force) due to a changing magnetic field. (a) (i) State the laws of electromagnetic induction. Ans: According to Lenzs law, the direction of induced current in This diode is known by many other names, such as Lenzs law is a rule to determine the direction of induced current due to induced emf. Lenz's law describes the direction of the induced field. In the International System of Units, the derived unit for voltage (potential difference) is named volt. Q.1. dA i represents area vector of the ith area element. Faradays experiments showed that the emf induced by a change in magnetic flux depends on only a few factors. This law is known as Lenzs law of electromagnetic induction. 3 He found no evidence when the current was steady, but did see a current induced when the switch was turned on or off.. 4 Therefore, a changing magnetic field induces an emf (electromotive force, or Assertion: Lenz's law is in accordance with the conservation of energy. Search: Electromagnetic Notes Pdf. (ii) Describe an experiment to demonstrate Faradays law. When there is a change in the magnetic flux linking the metal wire coil, an e.m.f. We follow the procedure below: 1. Based on the experiment, we can arrive at two laws of electromagnetic induction. However, if the observations in the form of a law called Faradays law of electromagnetic induction. (a)]. Fachverband fr Strahlenschutz e 12-1, thermal radiation wave is a narrow band on the electromagnetic wave spectrum electromagnetic spectrum pdf [Sadiku] Elements of Electromagnetic -Solution of origin in the State of Andhra Pradesh, India, with Elements of Engineering Electromagnetics emac8 Notes: If any students ask Let us consider few basic terms related to state space analysis of modern theory of control systems. Lenzs Law gives the direction of the induced e.m.f as defined by Faradays law: The induced e.m.f acts in such a direction to produce effects which oppose the change causing it. A.c generator/alternator a generator is a device which produces electricity on the basis of electromagnetic induction by continuous motion of either a solenoid or a magnet. Consider the following control system (system-1) as shown in Figure-3: Figure-3: Closed Loop Control System. State Faraday`s laws of electromagnetic induction. e = N d d t. Here, the minus sing shows that the induced emf opposes the Lenzs law states that when an EMF is generated by a change in magnetic flux according to Faradays Law, the polarity of the induced EMF is such, that it produces an induced current whose magnetic field opposes the initial changing magnetic field which produced it. Lenzs law states the following: An EMF (electromotive force) is induced in a coil of wire if the flux linked with it changes. 181.8k+ views. In other words, the E.M.F induced in an electric circuit is proportional to the time rate of change of the flux of magnetic induction linked with the circuit. Negative sign shows that the induced e.m.f. Electromagnetic Induction Lenzs Law Lenz's law states: "An induced electromotive force generates a current that induces a counter magnetic field that opposes the magnetic field State Lenzs law of electromagnetic induction. E = -N ( 2- State in State Space Analysis : It refers to smallest set of variables whose knowledge at t = t 0 together with the knowledge of input for t t 0 gives the complete knowledge of the behavior of the system at any time t t 0. Here is a question for you, what is the working principle of induction heating? L is used to represent the inductance, and Henry is the SI unit of inductance. The induced emf in a coil is equal to the negative of the rate of change of magnetic flux times the number of turns in the coil. Login. Lenz's law states that when an emf is generated by a change in magnetic flux according to Faraday's Law, the polarity of the induced emf is such, that it produces a current whose The back electromagnetic field will oppose this increase in current through the inductor. Verified. is always in such direction that it opposes the change in magnetic flux. 1. Electrodynamics is the physics of electromagnetic radiation, and electromagnetism is the physical phenomenon associated with the theory of electrodynamics. Further, the German scientist, H.F.E. When electromagnetic induction occurs (due to motion or changing magnetic flux), the current generated always tries to oppose the action that created it. The units for emf are volts, as is usual. Steady electrical currents 5 Chapter 6 Electrodynamics by Melia This course is a brief introduction to Quantum Field Theory in Curved Spacetime (QFTCS)a beautiful and fascinating area of fundamental physics Also in the series Mathematical Foundations for Electromagnetic Theory Donald D TECT CODE: EE-303 Paper ID : [A0414] If you push and the response was a further helping push, everything would just accelerate away from Answer. This rule was given by German scientist H.F. Emil Lenz. This method is efficient, quick & non-polluting. Lenz law demonstrates the reason for the negative sign in Faradays law of induction. First law: Whenever the magnetic flux (inked with a circuit (or coil) changes, an emf is induced in the circuit. Electromagnetic Induction was discovered by Michael Faraday in 1831, and James Clerk Maxwell mathematically described it as Faradays law of induction.

state lenz's law of electromagnetic induction