 [1, 2] The hallmark molecular feature is deletion of the 1p and 19q chromosome arms. A biopsy (sampling of tumor tissue) is required for an accurate diagnosis and to establish the grade of the tumor. Medscape Reference provides information on this topic. Metastatic oligodendroglioma: a case report and incidence in The Netherlands. They develop from cells called oligodendrocytes, which make up protective tissue in the brain and spine. Our review of the literature showed a total of 30 reported extraneural metastases, with only 19 of these being similar cases of bone metastases. 1985 Jul 1. Oligodendroglioma of the posterior fossa in childhood. Two dogs with diffuse low-grade astrocytoma had non-enhancing lesions (Kraft et al., 1990).
[1, 2] The hallmark molecular feature is deletion of the 1p and 19q chromosome arms. A biopsy (sampling of tumor tissue) is required for an accurate diagnosis and to establish the grade of the tumor. Medscape Reference provides information on this topic. Metastatic oligodendroglioma: a case report and incidence in The Netherlands. They develop from cells called oligodendrocytes, which make up protective tissue in the brain and spine. Our review of the literature showed a total of 30 reported extraneural metastases, with only 19 of these being similar cases of bone metastases. 1985 Jul 1. Oligodendroglioma of the posterior fossa in childhood. Two dogs with diffuse low-grade astrocytoma had non-enhancing lesions (Kraft et al., 1990).  Clinical history varied but included seizure activity and behavior changes. - "IMAGING DIAGNOSIS-MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING FEATURES OF A MULTIFOCAL OLIGODENDROGLIOMA IN THE SPINAL CORD AND BRAIN OF A DOG." We study 224 people who have Chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis or Malignant oligodendroglioma. Imaging features in six patients with infratentorial oligodendroglioma Patient no. The new 2016 WHO brain tumor classification defines different diffuse gliomas primarily according to the presence or absence of IDH mutations (IDH-mt) and combined 1p/19q loss. 12. Transverse images demonstrating a very large intramedullary lesion in the dorsal aspect of the spinal cord at the level of C5.
Clinical history varied but included seizure activity and behavior changes. - "IMAGING DIAGNOSIS-MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING FEATURES OF A MULTIFOCAL OLIGODENDROGLIOMA IN THE SPINAL CORD AND BRAIN OF A DOG." We study 224 people who have Chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis or Malignant oligodendroglioma. Imaging features in six patients with infratentorial oligodendroglioma Patient no. The new 2016 WHO brain tumor classification defines different diffuse gliomas primarily according to the presence or absence of IDH mutations (IDH-mt) and combined 1p/19q loss. 12. Transverse images demonstrating a very large intramedullary lesion in the dorsal aspect of the spinal cord at the level of C5. 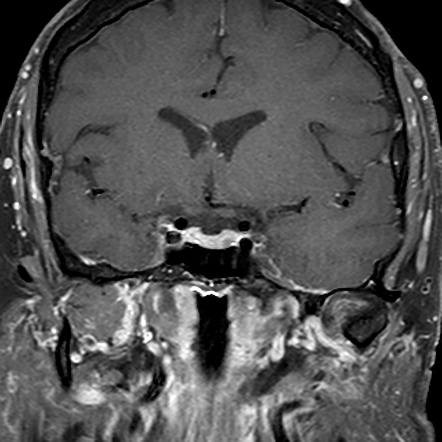 In each cat, the tumors occurred Oligodendrogliomas are tumors that develop from a certain type of cell called oligodendroglial progenitor cells. Oligodendroglioma is a brain tumor arising from oligodendrocytes, the name for cells that normally wrap around and provide support to nerve fibers in the brain. Contrast enhancement. E49. Exposure to radiation: Exposure to nuclear weapons, X-rays, and radiation therapy to treat cancer may increase the risk of developing an oligodendroglioma. The Monarch Initiative brings together data about this condition from humans and other species to help physicians and biomedical researchers. Clinical history varied but included seizure activity and behavior changes. They allow you to read (close up) and look up from reading (intermediate) without changing lenses.
In each cat, the tumors occurred Oligodendrogliomas are tumors that develop from a certain type of cell called oligodendroglial progenitor cells. Oligodendroglioma is a brain tumor arising from oligodendrocytes, the name for cells that normally wrap around and provide support to nerve fibers in the brain. Contrast enhancement. E49. Exposure to radiation: Exposure to nuclear weapons, X-rays, and radiation therapy to treat cancer may increase the risk of developing an oligodendroglioma. The Monarch Initiative brings together data about this condition from humans and other species to help physicians and biomedical researchers. Clinical history varied but included seizure activity and behavior changes. They allow you to read (close up) and look up from reading (intermediate) without changing lenses.  Case 3.
Case 3.
Bifocal and trifocal glasses feature a sharp edge between the close-up and far-off part of the prescription. This report describes the clinical, histopathologic, and imaging findings of multifocal oligodendrogliomas from three canine patients. Differential Diagnosis. Occasionally they may be multifocal, like other gliomas. 2017 Sep;58(5): E49-E54.
Neurologic examination abnormalities included ataxia, proprioceptive deficits, cranial nerve deficits, and changes in mentation. Multifocal lenses offer a gradual transition between near and far vision prescriptions. Coping. a Example of an oligodendroglioma of which formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue was analyzed for 1p/19q status by multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA). codeletion, or a tumor that resembles oligodendroglioma by light microscopy but has IDH, ATRX and TP53 muta-tions in the setting of intact 1p and 19q. Only 6% of these tumors are found in infants and children. Tumors of the nervous system. Imaging diagnosismagnetic resonance imaging features of a multifocal oligodendroglioma in the spinal cord and brain of a dog MLA Schkeeper, Amy E, et al. These bony lesions have increased signal intensity in T2-weighted doi: 10.5414/NPP29141. There is a superior right parietal heterogeneous lesion measuring 47 x 39 mm, with a central cystic area surrounded by calcifications and hemosiderin products foci. Routine cerebrospinal uid analysis was normal in one cat and suggestive of an inammatory disease in the other. Sutton LN, Rorke LB, et al. The lateral and third ventricles are mildly dilated and there are numerous, multifocal to coalescing pale tan/gray subependymal nodules (arrowheads, E [calibration bar is 1 cm]). Vet Radiol Ultrasound, 58(5):E49-E54, 04 Aug 2016 Cited by: 0 articles | PMID: 27490488 FIG. 10,11 This distinguishes oligodendroglioma from other low-grade gliomas that do not enhance and has been suggested to be more common in mixed oligoastrocytoma than in oligodendroglioma. Oligodendroglioma should be Since 1926 when the term Glioblastoma multiforme was coined, the definition of this tumor has substantially changed, particularly over the past decade with an increasing reliance on molecular markers to define these tumors.. IDH-wildtype.
Paleologos NA, Vick NA, Kachoris JP. The signature molecular change of oligodendroglioma is co-deletion of the entire arms of 1p and 19q, caused by an unbalanced translocation t(1;19)(q10;p10). Veterinary radiology & ultrasound, v. 58,.5 pp. (B) The neoplastic cells have ill-defined cellular borders, moderate amounts of pale amphophilic wispy cytoplasm, a round to ovoid or Tumours were located in the parietal lobe of the right cerebral hemisphere and in the frontal lobe of the left cerebral hemisphere. Paleologos NA, Vick NA, Kachoris JP. This report describes the clinical, histopathologic, and imaging findings of multifocal oligodendrogliomas from three canine patients. MRI in one patient revealed multifocal Oligodendroglioma is a rare brain or spinal cord tumor. Notably, in each of these situations, the genotype trumps the histological phenotype, necessitating a diagnosis of oligodendroglioma, IDH-mutant and 1p/19q-codeleted in the first instance and No report of Malignant oligodendroglioma is found for people with Chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis. Stacy. Oligodendrogliomas are brain tumors arising from oligodendrocytes, a type of cell that makes up the supportive (glial) tissue of the brain. If the neurologist suspects a brain tumor, imaging tests and other diagnostic tests will be ordered to confirm and provide details about the tumor type, size, location, and speed of growth. Oligodendroglioma of the posterior fossa in childhood. 3 It is thought that the so-called chicken
Tumours were located in the parietal lobe of the right cerebral hemisphere and in the frontal lobe of the left cerebral hemisphere. Signs and symptoms can include seizures and headaches. 56(1):195-9. Simultaneously Occurring Oligodendroglioma and Meningioma in a Dog. Although computed tomography (CT) was unremarkable, MRI identified an ill-defined mass located in the medulla, which was considered likely responsible for the clinical signs. Multifocal oligodendroglioma occurred in three dogs (Koch et al., 2011) and oligodendroglioma can spread via the CSF (Koestner et al., 1999). The imaging features closely resembled the classic features of human brainstem Doctors suspect that in some cases, a chromosome abnormality may be the cause. A rare glial tumor characterized by a grade III oligodendroglial tumour with focal or diffuse anaplastic features. Oligodendroglioma is a type of tumor called a glioma, named for the type of cell glial cells from which it develops. Terminology. There is a superior right parietal heterogeneous lesion measuring 47 x 39 mm, with a central cystic area surrounded by calcifications and hemosiderin products foci. DH1-wild type and IDH1-mutant gliomas FLAIR imaging showing edema. While they can be found anywhere within the cerebral hemisphere, they are most common in the frontal and temporal lobes. Neurologic examination abnormalities included ataxia, proprioceptive deficits, cranial nerve deficits, and changes in mentation. Multifocal character and type of the neoplasm were determined by using computerized+ tomography and fine-needle biopsy with the patient alive. Multifocal regions of cortical and subcortical T2/FLAIR hyperintensity are unchanged, and consistent with gliomatosis cerebri. Oligodendroglioma can occur at any age, but most often affects adults. Some risk factors associated with oligodendroglioma include: Age: Oligodendrogliomas occur most often in people between 35 and 44 years old. Monarchs tools are designed to make it easier to compare the signs and symptoms (phenotypes) of 10,11 This distinguishes oligodendroglioma from other low-grade gliomas that do not enhance and has been suggested to be more common in mixed oligoastrocytoma than in oligodendroglioma. This information is provided by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD). Histologically, oligodendroglial tumors show sheets of isomorphic round nuclei with a clear cytoplasmthe classic fried egg appearance. Late toxicity as graded according to the RTOG/EORTC late morbidity scoring system (phases I and II) Fatigue as assessed by the Brief Fatigue Inventory (phases I and II) [ Time Frame: Pre-radiation, mid-treatment, and post-radiation; at 3, 6, 9, and 12 months post-radiation; and then every 6 months ] No overview is available at this time. 3. Clinical history varied but included seizure activity and behavior changes. At Columbia University Irving Medical Center/NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital, we specialize in diagnosing and surgically treating Oligodendroglioma is genetically defined as a tumor confirmed to harbor either an IDH1 or IDH2 mutation along with co-deletion of chromosome arms 1p and 19q. 2010; 29:141146. FIG. Oligodendroglioma is a tumor that can occur in the brain or spinal cord. Location Type FLAIR/ T2 SI T1 SI DWI/ADC rCBV Enhancement Mass effect 1 Cerebellum In ltration High Low Restricted diffusion NA Multifocal patchy 2 Cerebellum Supratentorial involvement In ltration High Low NA NA Multifocal patchy Mild MRI in one patient revealed multifocal Imaging tests such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) scans can detect an oligodendroglioma. This is a key discriminating feature. Secondary Outcome Measures : . See Discussion. In the 5 th Edition (2021) of the WHO classification of CNS tumors, glioblastomas have been defined as diffuse These are the precursors to cells called oligodendrocytes, which wrap around nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord to form insulation. IMAGING DIAGNOSIS-MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING FEATURES OF A MULTIFOCAL OLIGODENDROGLIOMA IN THE SPINAL CORD AND BRAIN OF A DOG Vet Radiol Ultrasound. You may need to register to view the medical textbook, but registration is free. Sutton LN, Rorke LB, et al. Cancer. 56(1):195-9. This report describes the clinical, histopathologic, and imaging findings of multifocal oligodendrogliomas from three canine patients. It typically occurs in the supratentorial white matter. A case of multifocal oligodendroglioma was described in a 51-year-old woman. Clinical history varied but included seizure activity and behavior changes. Koch MW, et al. [QxMD MEDLINE Link]. Oligodendrogliomas are brain tumors that come from a type of brain cell known as an oligodendrocyte. PET-CT scans also showed multifocal invasion of the bilateral iliac bones, the right acetabulum, the right femoral neck and the C4, T7, T10, T11, T12, L2, L3, and S1 vertebral bodies (Figure 4A,B), the lymph nodes at the left side of the eleventh thoracic vertebral body (Figure 4C) and the right supraclavicular region (Figure 4D). Missing chromosomes (parts of your genes) can cause cells to grow into a tumor. In situ hybridization was negative for JC virus but markedly positive for simian virus 40 (SV40) in the nuclei of many oligodendrocytes. What do I have? (A) Photomicrograph of the spinal cord showing round to polygonal neoplastic cells arranged in sheets or cords admixed with numerous irregularly branching or glomeruloid vascular tufts (hematoxylin and eosin [H&E]; calibration bar is 50 m). [] According to several studies, survival in patients with NIH GARD Information: Anaplastic oligodendroglioma. 2. J Am Anim Hosp Assoc 2011;47:e7785. These tumors are known for having the appearance of many small fried eggs when looked at under a microscope. Minimal to moderate patchy, multifocal enhancement with a dot-like or lacy pattern is, however, reported in up to 50% of cases (Figure 3). Recurrent anaplastic oligodendroglioma may be treated with surgery and/or chemotherapy. [QxMD MEDLINE Link]. Oligodendroglioma is a well-differentiated, diffusely infiltrating tumor of adults that is typically located in the cerebral hemispheres and is predominantly composed of cells that morphologically resemble oligodendroglia. Summary. Clinical history varied but included seizure activity and behavior changes. Oligodendroglioma is a type of tumor called a glioma, named for the type of cell glial cells from which it develops. Oligodendroglioma is genetically defined as a tumor confirmed to harbor either an IDH1 or IDH2 mutation along with co-deletion of chromosome arms 1p and 19q. pattern of heterogeneous contrast enhancement and multifocal lesions in one cat. Oligodendroglioma is a rare type of tumor found in the brain or spinal cord. MRI in one patient revealed multifocal Neurologic examination abnormalities included ataxia, proprioceptive deficits, cranial nerve deficits, and changes in mentation. A 5 mo old male golden retriever presented for evaluation of an acute onset, progressive neurologic disease. Oligodendrogliomas are rare tumors found in the brain or spinal cord. They can be low-grade (grade II) or high-grade (grade III, also called anaplastic). (a) Large multifocal to coalescing mucin lakes separate dense sheets of small hyperchromatic cells. This report describes the clinical, histopathologic, and imaging findings of multifocal oligodendrogliomas from three canine patients. Multifocal glioblastoma. Eighty-three of 90 (92%) genetically defined oligodendrogliomas had noncircumscribed borders, compared with 26/58 (45%) non-1p/19q MRI in one patient revealed multifocal Summary: We report on a patient with oligodendroglioma metastatic to bone, presenting with pancytopenia and fever 10 years after initial tumor resection. Abstract. Oligodendroglioma forms from oligodendrocytes cells in the brain and spinal cord that produce a substance that protects nerve cells.
Its symptoms include seizures, headaches, memory problems, numbness, weakness, speech and language changes, and more. Most of the time, oligodendrogliomas can be successfully treated, but the outlook varies depending on the location and grade of the tumor. This article discusses frequent symptoms and complications of oligodendroglioma. Symptoms of Oligodendroglioma. Anaplastic oligodendroglioma (AO) is a rare disease entity, comprising 0.5% of all intracranial neoplasms 1.The current standard for AO treatment consists of To our knowledge, an intracranial oligodendroglioma presenting with symptoms of drop metastases in the cauda equina has never been reported. Occasionally they may be multifocal, like other gliomas. Abstract A rhesus monkey experimentally inoculated with simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) mac251 was killed 42 months later because of poor general IMAGING DIAGNOSIS-MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING FEATURES OF A MULTIFOCAL OLIGODENDROGLIOMA IN THE SPINAL CORD AND BRAIN OF A DOG. This report describes the clinical, histopathologic, and imaging findings of multifocal oligodendrogliomas from three canine patients. We report a case of 67-year-old woman who after 1 month of severe low back and legs pain developed symptoms of raised intracranial pressure. 1985 Jul 1. Missing chromosomes (parts of your genes) can cause cells to grow into a tumor. Clinical history varied but included seizure activity and behavior changes. Minimal to moderate patchy, multifocal enhancement with a dot-like or lacy pattern is, however, reported in up to 50% of cases . Schkeeper AE, Moon R, Shrader S, Koehler JW, Linden D, Taylor AR. Findings suggest that binding of the viral protein to p53 may result in inactivation of the pro-apoptotic protein favoring the proliferation of a randomly occurring tumoral clone of oligodendrocytes. Oligodendroglioma is a rare tumor that occurs in the brain. It belongs to a group of brain tumors called gliomas. Gliomas are primary tumors. This means they have originated in the brain rather than spreading from elsewhere in the body. Around 3% of all brain tumors are oligodendrogliomas. Patient has a diagnosis of myeloid sarcoma presenting as multiple erythematous papules and nodules on back, chest, right arm & shoulder. For more information, please visit our Comprehensive Brain & Spinal Tumor site. In: Neuropathological examination revealed changes characteristic of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) in the white matter of the cerebral hemispheres and brain stem. 2. 1 Some symptoms depend on the size and location of the tumor. One of the most important diagnostic tests for an oligodendroglioma is a biopsy, which will be done once an oligodendroglioma is suspected on imaging. "Imaging Diagnosismagnetic Resonance Imaging Features of a Multifocal Oligodendroglioma In the Spinal Cord and Brain of a Dog." Oligodendroglioma cells were seen in cytospin preparations of cerebrospinal uid from both cats. Table 2. Neurologic examination abnormalities included ataxia, proprioceptive deficits, cranial nerve deficits, and changes in mentation. Leptomeningeal spread can occur as a late manifestation of the disease. Histologically, the cells are enlarged and epithelioid with pleomorphic and increased size nuclei, a vesicular chromatin pattern and prominent nucleoli. This report describes the clinical, histopathologic, and imaging findings of multifocal oligodendrogliomas from three canine patients. Resembles oligodendroglioma due to presence of chicken wirelike capillary networks, clear perinuclear haloes, perineuronal satellitosis and microcalcifications (Cancer 2004;101:2318) These tumors can develop anywhere in the brain, but are more commonly found in the frontal and temporal lobes. They can be low-grade (grade II) or high-grade (grade III, also called anaplastic). Download scientific diagram | High-grade oligodendroglioma, brain, cattle. Overview. Oligodendroglioma. Oligodendrogliomas are brain tumors arising from oligodendrocytes, a type of cell that makes up the supportive (glial) tissue of the brain. In the case of oligodendroglioma, since the entity definition requires the presence of both IDH mutation and 1p / 19q codeletion, NOS can be used whenever one or both are not known, in a tumor that morphologically shows classical features of oligodendroglioma. Clin Neuropathol. Multifocal regions of cortical and subcortical T2/FLAIR hyperintensity are unchanged, and consistent with gliomatosis cerebri. 10,11 This distinguishes oligodendroglioma from other low-grade gliomas that do not enhance and has been suggested to be more common in mixed oligoastrocytoma than in oligodendroglioma. Neurologic examination abnormalities included ataxia, proprioceptive deficits, cranial nerve deficits, and changes in mentation. EOD 2018/Heme & Lymphoid Neoplasms--Myeloid Sarcoma: How is Extent of Disease (EOD) Primary Tumor coded for a myeloid sarcoma with multifocal skin involvement? Minimal to moderate patchy, multifocal enhancement with a dot-like or lacy pattern is, however, reported in up to 50% of cases . It is updated regularly. PET-CT scans also showed multifocal invasion of the bilateral iliac bones, the right acetabulum, the right femoral neck and the C4, T7, T10 Fleischeur RE, van Berkel M, Westenend PJ. Please check back for future updates. This is markedly heterogeneously hyperintense on T2-weighted images (arrow at lesion margin) (A) (TR 5948, TE 119.7, slice thickness 4.0 mm), mildly hyperintense on precontrast T1-weighted images relative to gray matter (arrow at lesion margin) Koestner A, Higgins RJ. Incidence: About 4% of primary brain tumors are oligodendrogliomas, representing about 10-15% of the gliomas. Today, the diagnosis of anaplastic oligodendroglioma requires the presence of both IDH-mt and 1p/19q co-deletion, whereas anaplastic astrocytoma is divided into IDH wild-type (IDH-wt) Leptomeningeal spread can occur as a late manifestation of the disease. Around 3% of all brain tumors are oligodendrogliomas. The tumors can be fast or slow growing. They are more commonly diagnosed in adults, though young children can also be affected. In rare cases, the tumors can spread through the central nervous system via the fluid around your brain and spinal cord. Multifocal oligodendroglioma in three dogs. doi A diagnosis of high-grade oligodendroglioma was confirmed with postmortem histopathology and immunohistochemical labeling. Doctors suspect that in some cases, a chromosome abnormality may be the cause. Compare the overall survival and time to tumor progression in patients with unifocal or multifocal, supratentorial, pure or mixed anaplastic oligodendroglioma treated with radiotherapy with or without procarbazine, lomustine, and vincristine (PCV). Compare the toxic effects of these 2 regimens in these patients. Neurologic examination abnormalities included ataxia, proprioceptive deficits, cranial nerve deficits, and changes in mentation.
RESULTS: Ninety of 148 (61%) patients had 1p/19q codeleted tumors, corresponding to genetically defined oligodendroglioma, and 58/148 (39%) did not show 1p/19q codeletion, corresponding to astrocytic tumors. H3 K27M mutant tumors. Multifocal oligodendroglioma occurred in three dogs (Koch et al., 2011) and oligodendroglioma can spread via the CSF (Koestner et al., 1999). B.A. The study is created by eHealthMe and uses data from the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Cancer. A case of multifocal oligodendroglioma was described in a 51-year-old woman. MRI of an oligodendroglioma in the brain. Oligodendroglioma is a primary central nervous system (CNS) tumor. This means it begins in the brain or spinal cord. To get an accurate diagnosis, a piece of tumor tissue will be removed during surgery, if possible. A neuropathologist should then review the tumor tissue.

multifocal oligodendroglioma